Overview
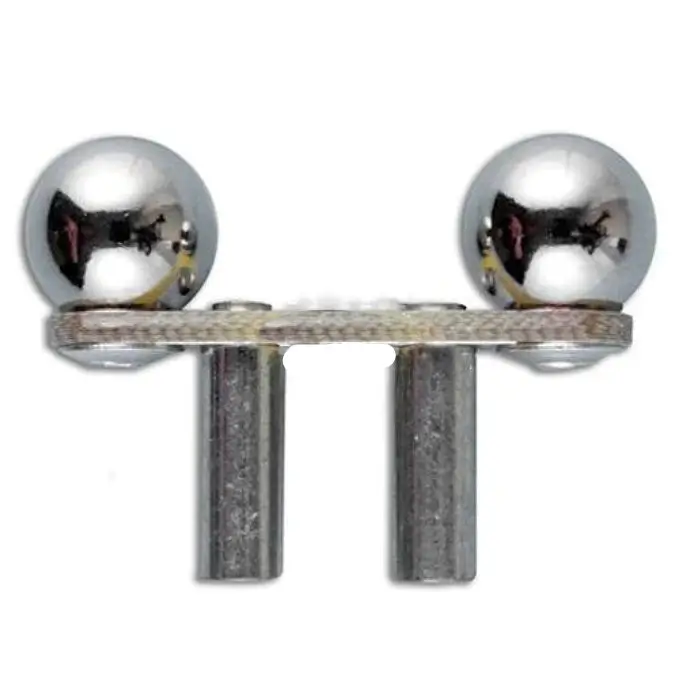
Diagnostic ball probes are specialized electrodes designed for use with peripheral nerve stimulators (PNS) to accurately locate and assess nerve function during medical procedures. These probes deliver controlled electrical stimulation, helping clinicians identify nerve pathways, verify nerve integrity, and minimize surgical risks. They are essential tools in anesthesiology, pain management, and surgical nerve monitoring.
Key Features
1. Precision Nerve Stimulation
- Designed with a rounded ball tip for optimal tissue contact and controlled current delivery.
- Enables focused stimulation to distinguish between motor and sensory nerves.
2. Sterile & Ergonomic Design
- Disposable or reusable options available, ensuring sterility in surgical settings.
- Lightweight and easy to maneuver, allowing for precise placement during procedures.
3. Compatibility with Nerve Stimulators
- Works seamlessly with standard peripheral nerve stimulators (e.g., 2Hz–5Hz stimulation range).
- Some models feature insulated shafts to prevent unintended current leakage.
4. Adjustable Stimulation Parameters
- Supports variable current intensity (typically 0.1mA–5.0mA) for fine-tuned nerve detection.
- Helps determine minimum threshold current for nerve response, improving procedural accuracy.
Applications
1. Regional Anesthesia & Nerve Blocks
- Assists in locating target nerves before administering anesthesia (e.g., brachial plexus, sciatic nerve blocks).
- Reduces the risk of intraneural injection by confirming needle proximity to nerves.
2. Intraoperative Nerve Monitoring
- Used in orthopedic, neurosurgical, and ENT procedures to prevent nerve damage.
- Helps surgeons verify nerve preservation during tumor resections or decompression surgeries.
3. Diagnostic Nerve Testing
- Assesses nerve functionality in patients with neuropathy or nerve injuries.
- Aids in differentiating between intact and damaged nerves in trauma cases.
Who Uses Diagnostic Ball Probes?
- Anesthesiologists – For precise nerve block placement.
- Surgeons – To avoid nerve injury during delicate operations.
- Neurologists & Pain Specialists – For diagnostic nerve conduction assessments.
- Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation (PM&R) Doctors – In electrodiagnostic studies.
Conclusion
Diagnostic ball probes are critical for safe and accurate nerve localization in both surgical and diagnostic settings. Their ability to deliver controlled electrical stimulation enhances procedural precision, reduces complications, and improves patient outcomes. Whether used for anesthesia, surgery, or diagnostics, these probes ensure reliable nerve identification while minimizing risks.




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.